8 things you need to know about steel and wind energy
Do you know how steel contributes significantly to green energy? Ever wondered how long a wind turbine last and what happens after it is decommissioned?
You will find below 8 things you need to know about steel and wind energy.
1. How much steel is there in a windmill?
Between the towers, foundations, generator, Gearbox, Yaw & Pitch, steel is used to create more than 80% of the components required to build a typical wind turbine.
2. Is steel environmentally friendly and sustainable?
Steel is very friendly to the environment.
It is completely recyclable, possesses great durability, and, compared to other materials, requires relatively low amounts of energy to produce. Innovative lightweight steel construction (such as in automobile and rail vehicle construction) help to save energy and resources. The steel industry has made immense efforts to limit environmental pollution in the last decades. Energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions have decreased to half of what they were in the 1960s. Dust emissions have been reduced by even more.
3. Can steel be easily recycled?
Yes, steel is the world's most recycled material and its unique magnetic properties make it an easy material to recover from the waste stream to be recycled. The properties of steel remain unchanged no matter how many times the steel is recycled. The electric arc furnace (EAF) method of steel production can use exclusively recycled steel.
More information: Recycling of steel
4. Is wind energy really sustainable?
The steel industry has an important role to play in clean production technologies. Unlike power generation based on fossil fuels, a wind farm does not emit any CO2. Also, the energy used to build, operate and dismantle a typical turbine is recovered within the first few months of operation. Regarding the materials, steel is used to create more than 80% of the components required to build a wind turbine. Valued for its strength, flexibility and durability in the field, steel is also 100% recyclable, making wind energy truly renewable.
5. What are a turbine’s lifetime emissions?
Wind turbines produce no greenhouse gas emissions during their operation. It takes a turbine just three to six months to produce the amount of energy that goes into its manufacture, installation, operation, maintenance and decommissioning after its 20-25 year lifetime. During its lifetime a wind turbine delivers up to 80 times more energy than is used in its production, maintenance and scrapping. Wind energy has the lowest ‘lifecycle emissions’ of all energy production technologies.
Source: http://www.ewea.org/
6. How long does a wind turbine work for?
Wind turbines can carry on generating electricity for 20-25 years. Over their lifetime they will be running continuously for as much as 120,000 hours. This compares with the design lifetime of a car engine, which is 4,000 to 6,000 hours.
Source: http://www.ewea.org/
7. What happens to wind turbines after decommissioning?
From a climate change and sustainability perspective, it is important to take into account the life cycle of products. Part of the application process for permits to build wind farms often requires an explanation of how the developer plans to manage the site into the future. Consequently, re-use and recycling are of great importance. The application of steel in most of the key components of wind turbines makes it possible for the wind energy industry to meet the technical requirements of the turbines and climate change demands at the same time.
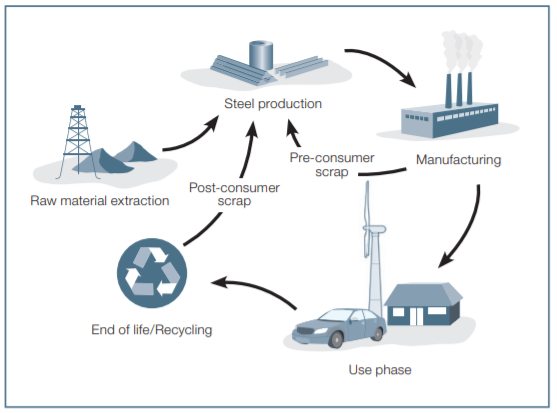
Source: Worldsteel
8. What other environmental benefits does wind power bring?
Wind energy emits no toxic substances such as mercury and air pollutants like smog-creating nitrogen oxides, acid rain-forming sulphur dioxide and particulate deposits. These pollutants can trigger cancer, heart disease, asthma and other respiratory diseases, can acidify terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, and corrode buildings.
Wind energy creates no waste or water pollution. Unlike fossil fuel and nuclear power plants, wind technology uses very little water to produce electricity. Given the fact that water scarcity is pressing and will be exacerbated by climate change and population growth, wind energy is key to preserving water resources.
Source: http://www.ewea.org/
